- AIXBIO
- Posts
- AIXBIO Weekly #18 - Nov/06/2023
AIXBIO Weekly #18 - Nov/06/2023

Regulatory Landscape
U.S. Aims for Global Leadership & Enhanced Safety in AI with New Executive Order
President Biden's Executive Order on AI outlines a framework for the development and use of artificial intelligence in the United States, with an emphasis on safety, security, and ethical standards.
The order requires developers of significant AI systems to disclose safety test results to the U.S government, aiming to enhance transparency and build trust in AI technologies. It sets forth safety protocols, creates an AI Safety and Security Board, and addresses vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
The directive also seeks to protect against AI-facilitated biological threats and financial fraud, while leveraging AI to improve cybersecurity. It prioritizes the protection of individual privacy, the promotion of equality and civil rights, and the support of consumers and workers.
USAISI, led by NIST, to set AI safety & trust standards, ensuring advanced AI model evaluation. Collaborations with global institutes & industries planned
However, the order has faced criticism for its potential impracticalities and negative implications. Critics point out the lack of clarity in defining what constitutes a national security risk, suggesting that social media platforms could present more significant threats than AI models themselves. The mandate for watermarking AI-generated content is viewed as a possible obstacle for the development of vision AI technologies.
Questions have been raised about the feasibility of enforcing testing requirements for AI models, especially those developed outside the U.S. The privacy measures have been described as potentially more restrictive than those applied to search engines, which could put AI models at a disadvantage. Over the long term, there are concerns that the order might adversely affect companies that develop foundational models, particularly in the field of vision AI. The regulation is seen as potentially unfavorable for firms like OpenAI, while possibly benefiting traditional search engines due to the uneven application of these new rules.
EO, pertaining to the biotech & healthcare sector:
AI Safety in Biotech: Prioritizes the creation of safe and secure AI systems, particularly in biotechnology, to mitigate risks before deployment.
Healthcare Consumer Protection: Enforces consumer protection laws against AI-related fraud and biases in healthcare, ensuring equitable treatment.
National Security: Develops AI evaluation tools for assessing threats in biological and chemical domains, relevant to health security.
Equity in Healthcare AI: Aims to prevent AI from exacerbating discrimination in healthcare, promoting uses that enhance quality of life.
Privacy Protections: Stresses the importance of safeguarding privacy and civil liberties in the advancement of AI, especially with health data.
AI Workforce Development: Focuses on job training in healthcare to adapt to AI advancements, aiming to improve job quality and safety.
Biosecurity Measures: Introduces tools to evaluate AI systems that could pose biosecurity threats, ensuring responsible use in health-related areas.
Synthetic Biology: Addresses the role of AI in synthetic biology, which involves genetic redesigning of organisms for medical advancements.
The Bletchley Declaration: A Global Commitment to Safe and Responsible AI Development
The Bletchley Declaration, stemming from the AI Safety Summit of 2023, is a global pledge by attending nations to ensure the safe and responsible development and use of Artificial Intelligence (AI). It acknowledges AI's transformative potential to enhance human life and the necessity of its human-centric, trustworthy deployment for the benefit of all.
The declaration recognizes AI's pervasive role in daily life and the unique opportunity to shape its development for public services and sustainable development goals.
The declaration places special emphasis on 'frontier' AI systems, which include highly capable general-purpose models that could perform a wide variety of tasks and potentially cause harm. It calls for intensified cooperation to understand and mitigate risks, particularly those that are international in nature.
All stakeholders, including governments, private companies, civil society, and academia, are urged to collaborate on ensuring AI safety. This includes transparency and accountability in safety testing and mitigating harmful capabilities. The declaration sets an agenda focusing on identifying AI safety risks, building a shared scientific understanding, and developing respective risk-based policies.
Navigating the Patent Maze in AI-Driven Drug Discovery
AI's role in drug discovery grows, yet patenting algorithms remains complex.
Investors are channeling billions into AI for drug discovery, with significant advancements evidenced by over 70 AI-derived molecules and vaccines undergoing clinical trials. The burgeoning field has seen a surge in deals, yet the commercial viability and clinical efficacy of these AI-derived candidates remain to be validated.
Insilico Medicine, a leader in the space, has demonstrated AI's potential by nominating a drug candidate in a fraction of the traditional time and cost. However, the intellectual property landscape for AI algorithms is fraught with complexity. Patenting such algorithms is not straightforward due to legal interpretations that often view them as abstract ideas rather than concrete processes. The decision to patent involves weighing the benefits against the costs and risks, including legal uncertainties and the potential for litigation. Despite the challenges, patents play a crucial role in protecting innovations and providing business security. The article underscores the strategic considerations companies must navigate in deciding whether to patent AI systems, publish their work, or keep it as a trade secret. The dynamic and fast-evolving nature of AI in drug discovery presents both opportunities and challenges for companies seeking to stake their claims in this frontier.
Innovation
Next-gen AlphaFold
Next-gen AlphaFold unveiled: enhanced accuracy & expanded molecular coverage, setting new standards in biomolecular predictions & aiding biomedical breakthroughs. A leap towards 'digital biology'
The latest iteration of AlphaFold, developed by Google DeepMind and Isomorphic Labs, marks a significant advancement in biomolecular predictions, showcasing remarkable accuracy and an expanded range of capabilities. Since its inception in 2020, AlphaFold has been a revolutionary tool in understanding proteins and their interactions. The new model extends its prowess beyond proteins, encompassing a variety of biological molecules, including ligands, nucleic acids, and those with post-translational modifications. This expansion is crucial for delving deeper into cellular mechanisms and has applications in disease pathway analysis, genomics, and drug design, among others.
The model’s ability to generate predictions for nearly all molecules listed in the Protein Data Bank, often achieving atomic accuracy, is a testament to its enhanced capabilities. Furthermore, it has set new benchmarks in protein-ligand structure prediction, outperforming existing docking methods and eliminating the need for reference protein structures or ligand pocket location information.
This feature is invaluable for drug discovery, allowing for the exploration of novel proteins. The AlphaFold database, housing structure predictions for nearly all known proteins, has become a global resource, accessed by over 1.4 million users from 190 countries, aiding diverse research endeavors.
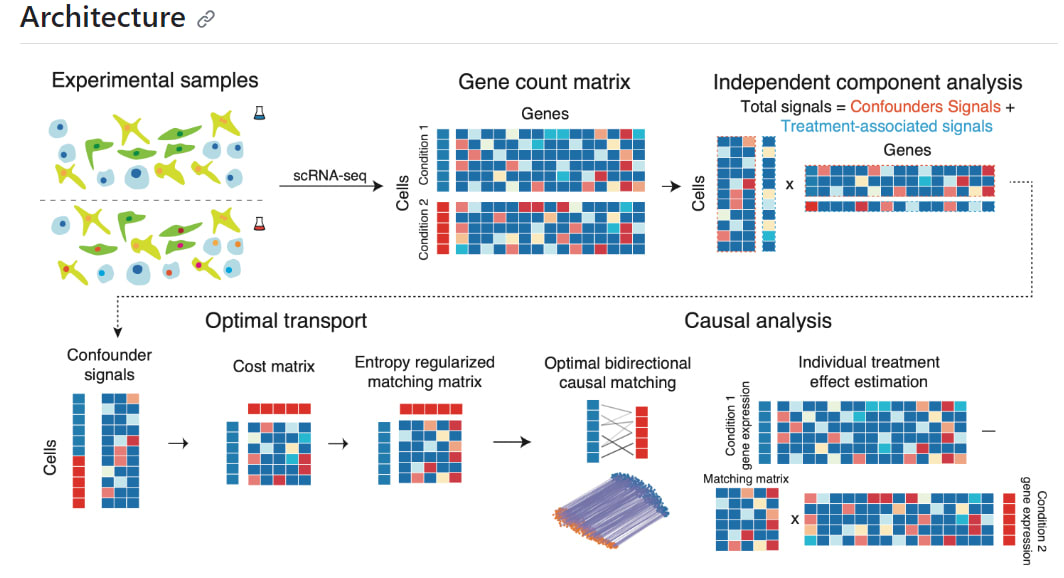
CINEMA-OT:
Uncovers the intricate communication system of immune cells through cytokines
The article from Yale University discusses groundbreaking research published in Nature Methods, which uncovers the intricate communication system of immune cells through cytokines. The study introduces a novel computational method, CINEMA-OT, based on causal inference to analyze how immune cells react to cytokine combinations.
Cytokines communicate in a synergistic manner, triggering unique gene activations. The team anticipates that global use of this technology will further decode immune system communications, propelling biological and medical discoveries. The significance of this research lies in its potential to transform our approach to treating diseases by manipulating immune responses more effectively. The study's insights into cellular communication could lead to breakthroughs in immunotherapies and a better understanding of how environmental factors like smoking affect our body's defense mechanisms.
MSIntuit™ CRC :
Owkin's AI Diagnostic Leap: Precision Screening for Colorectal Cancer
A groundbreaking study published in Nature Communications has validated Owkin's AI diagnostic tool, MSIntuit™ CRC, as a highly sensitive pre-screening instrument for colorectal cancer. With a sensitivity of 96%, the tool proficiently identifies patients with microsatellite stable (MSS) tumors who are unlikely to respond to checkpoint inhibitor therapy, thus potentially circumventing the need for further screening. This innovation comes at a crucial time, as colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer worldwide, with a significant mortality rate.
The AI diagnostic's ability to accurately classify MSI and MSS patients could revolutionize the current screening workflow, allowing for more rapid and efficient patient screening. The study's robust methodology, including blind validation across multiple pathology labs and diverse slide scanners, underscores the diagnostic's clinical applicability and potential for widespread adoption.
Owkin's AI tool not only promises to enhance lab efficiency by addressing global pathology shortages but also aims to match patients with the most effective therapies, thereby embodying the principles of precision medicine.
BigHat Biosciences: Pioneering Antibody Innovation with AI-Driven Platforms
BigHat Biosciences leverages AI/ML for rapid antibody development, aiming to innovate therapeutics.
BigHat Biosciences, a biotech firm in San Mateo, California, is at the forefront of integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with wet lab technologies to expedite the development of therapeutic antibodies. Their Milliner platform embodies this integration, enabling rapid cycles of design, testing, and development of antibodies.
The company's facility, equipped with a fleet of robots and a proprietary laboratory information management system, facilitates the production and characterization of approximately 800 molecules weekly—a number they plan to double. This rapid iteration is part of BigHat's strategy to explore new molecular spaces, potentially revolutionizing antibody therapeutics.
BigHat's business strategy focuses on collaborations and internal pipeline development, particularly in oncology and inflammation. Notable collaborations include those with Merck and Amgen, leveraging BigHat's platform to tackle complex antibody design challenges. The acquisition of Frugi Biotechnology enhances their capabilities in cell-free protein synthesis, crucial for rapid antibody testing
FDA
FDA grants breakthrough status to Paige Lymph Node
An AI tool aiding pathologists in detecting breast cancer metastases
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted Breakthrough Device Designation to Paige Lymph Node, an innovative AI application developed by Paige. This tool is designed to assist pathologists in the detection of breast cancer metastases within lymph node tissue, marking it as the first AI application of its kind to receive such recognition from the FDA.
The Breakthrough Device Designation is reserved for technologies that promise more effective diagnosis or treatment of life-threatening or irreversibly debilitating diseases, especially when no approved alternatives exist or when the new technology offers significant advantages over existing approved options.
The AI application is based on a deep learning model trained on a vast dataset of over 32,000 digitized hematoxylin and eosin-stained lymph node slides, allowing it to detect the presence of metastases with high sensitivity.
The device highlights suspicious areas on the lymph node tissue slides, streamlining the pathologist's review process. This capability is particularly significant given the current demands and resource constraints in pathology.
Previously, Paige achieved a similar breakthrough designation for its Paige Prostate Detect, an AI application for identifying cancerous prostate tissue, which has become the first and only FDA-authorized digital pathology application to date. Additionally, Paige's FullFocus, a whole-slide image viewer, has been approved by the FDA for use in primary diagnosis.
Partnerships
Merck KGaA Forges New AI Alliances
To Expedite Drug Discovery in Oncology, Neurology, and Immunology
Merck KGaA, a leader in science and technology, has announced two significant AI-driven drug discovery collaborations. Partnering with BenevolentAI and Exscientia, the company aims to harness AI for designing and discovering novel drugs, particularly in oncology, neurology, and immunology. These collaborations are poised to produce several new clinical development candidates, potentially leading to first-in-class and best-in-class treatments.
The agreements focus on three initial targets, with the scope for more in the future. The partners will receive upfront payments, along with milestone payments and sales-based royalties. This initiative is part of Merck KGaA's broader strategy to enhance R&D productivity and pipeline output sustainably.
By systematically exploring data science and AI, Merck KGaA is looking to accelerate the discovery and delivery of breakthrough medicines. The integration of AI across R&D processes, from target identification to clinical trials and product lifecycle management, is expected to transform drug discovery and development, enabling the company to deliver new medicines to patients faster and with a higher success rate.
#Merck KGaA partners with @benevolent_ai & @exscientiaAI , leveraging #AI for faster, successful drug discovery in key health areas
The focus is on developing novel clinical drug candidates with potential in #oncology, #neurology, and #immunology.
#AI#ML#GenAI#drugdiscovery… twitter.com/i/web/status/1…
— AI X BIO (@AIXBIO)
1:35 PM • Nov 5, 2023
Generate:Biomedicines & Roswell Park Unite to Forge New Paths in Oncology with AI-Driven Cell Therapies
Generate:Biomedicines, in collaboration with Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, has embarked on a strategic partnership to advance the development of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapies, targeting solid tumors like ovarian cancer. This multi-year alliance is set to harness the power of generative AI to create optimized cell therapies, a promising yet challenging endeavor in oncology. The Generate Platform's AI capabilities combined with Roswell Park's expertise in cell therapy design and clinical development aim to bring forth best-in-class treatments.
The collaboration is a significant step in addressing the unmet needs in solid tumor treatments, building on the successes of CAR T-cell therapies in liquid tumors. The agreement includes shared research and development efforts and a profit-sharing model upon commercialization. Roswell Park, with its expanded cGMP facilities, will play a pivotal role in clinical trials.
Google Health
Advancing Health Equity: Google's Approach to Responsible AI Development
Google's Chief Health Equity Officer, Dr. Ivor Horn, emphasizes the potential of AI to advance health equity while acknowledging the risks of exacerbating inequities if not handled responsibly. The article outlines four key strategies to ensure AI development is equitable: integrating foundational health equity approaches like Community-based Participatory Research (CBPR) into design and evaluation, prioritizing diverse representation in data to avoid propagating biases, considering real-world use cases to reduce harm among marginalized populations, and fostering inclusive collaboration with experts across various fields.
One highlighted initiative is the Pangenome project, which aims to create a more diverse genomic map in partnership with the National Institutes of Health (NIH). This project is crucial because the current genomic map is based on a single sequence that fails to represent humanity's diversity. Google's work on AI to recognize more skin tones and improve camera features for everyone is cited as an example of striving for equitable AI models.
Google's Responsible AI Team and the Equitable AI Research Roundtable (EARR) Program are instrumental in taking a multidisciplinary approach to understand AI's impacts and apply those insights.
Google Research is at the forefront of integrating AI into healthcare, striving for solutions that are more personalized and accessible. Their work spans various domains, including aiding radiologists in detecting breast cancer and supporting diabetic retinopathy screening. The team has developed Med-PaLM, a large language model fine-tuned for medical purposes, which excelled in medical question answering tasks. This achievement is part of a broader effort to harness generative AI's potential in medicine, focusing on enhancing tool safety, accuracy, and equity.
Collaboration with healthcare providers and industry partners has been pivotal in bringing research into clinical practice. For instance, Google's partnership with Jacaranda Health in Kenya aims to refine fetal ultrasound AI models, while cooperation with Osaka University focuses on dermatology classifiers. These partnerships are instrumental in understanding how AI can support clinical workflows and ultimately improve global health outcomes.
Google's commitment to sharing its learnings is evident in its efforts to make AI tools like Open Health Stack and CXR Foundation available to health researchers and innovators. By doing so, Google empowers the creation of digital health solutions that can save time and enhance health outcomes. The company's vision for the future of healthcare is one where AI plays a significant role in making healthcare more accessible, accurate, and equitable.
Google is hosting a live conversation on AI's role in healthcare .The panel of experts will discuss the role of LLMs in healthcare , the potential future applications of Health AI, and how they approach AI development and deployment ethically and responsibly.
And
Precision medicine is evolving with AI & biomarkers leading the way. From CAR T-cell treatments to CRISPR, the field is expanding.
AI aids in trial efficiency & biomarkers offer targeted treatments. The future hinges on tech & data
Oath Care, has launched an app called Oath Care that aims to support new parents by connecting them with healthcare professionals and providing them with access to a generative AI tool called ParentGPT.
Powered by ChatGPT, offers advice and insights from a variety of experts and community members, helping new parents navigate the challenges of early motherhood. The app attempts to address the lack of adequate resources and support for new mothers, particularly those at risk of experiencing postpartum depression.
Frontier Model Forum appoints Chris Meserole as Exec. Director
Frontier Model Forum appoints Chris Meserole as Exec. Director & launches a $10M AI Safety Fund, backed by tech giants & philanthropy.
Focus on safe & responsible AI development. Engaging with broader community for AI's safe use.