- AIXBIO
- Posts
- AIXBIO Weekly #19 - Nov/13/2023
AIXBIO Weekly #19 - Nov/13/2023

Regulatory Landscape
Monica Bertagnolli: Leading NIH into a New Era Amid Complex Challenges
The U.S. Senate has confirmed Monica Bertagnolli as the new Director of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), which had been awaiting a permanent leader since Francis Collins stepped down in December 2021. Bertagnolli, a distinguished cancer surgeon and clinical trial expert, transitions from her roles at Harvard Medical School and the National Cancer Institute to lead the NIH.
Bertagnolli takes charge of the $47 billion NIH during a period of intense budgetary and political scrutiny. Her appointment comes with the responsibility of navigating the NIH through various challenges, including addressing concerns from both conservative and liberal lawmakers. Issues range from NIH funding for gender-affirming care and virus studies to pressures about high drug prices.
During her confirmation hearing, Bertagnolli emphasized her commitment to expanding NIH's innovations and clinical trials to diverse populations across the United States. She faces an immediate challenge in urging Congress to preserve NIH funding amidst conflicting budget proposals from the Senate and the House.
Navigating AI's Role in Healthcare Through WHO's Strategic Insights
The World Health Organization (WHO), in its global strategy on digital health, emphasizes the critical role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in revolutionizing healthcare. This strategy, developed in collaboration with various international organizations and authorities, aims to harness AI for enhancing clinical trials, medical diagnosis, treatment, and personalized care. The Focus Group on AI for Health (FG-AI4H), established by WHO and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), is pivotal in exploring regulatory considerations for AI in healthcare.

This comprehensive approach is not intended as a regulatory framework but serves as a vital resource for stakeholders, including developers, regulators, manufacturers, and health practitioners.
It outlines six key areas: documentation and transparency, risk management, validation, data quality, privacy, and collaboration. The emphasis is on a risk-based approach and the necessity of transparent documentation throughout the AI system's lifecycle.
Silicon Valley Divided: The Debate Over AI Regulation
While government officials and leaders from Big Tech companies have reached a consensus on the need for regulatory frameworks for AI, there is significant pushback from other tech sectors. Influential venture capitalists, CEOs of midsize companies, and advocates for open-source technology are expressing concerns that stringent regulations could quash competition in this burgeoning field.
The debate highlights a fundamental tension between the desire for safety and ethical considerations in AI development and the fear that regulation could stifle innovation and growth. Proponents of regulation argue that, without it, the rapid advancement of AI could lead to unforeseen and potentially harmful consequences. On the other hand, critics of regulation worry that it could give an unfair advantage to established players and limit the entry of new innovators.
The debate over AI regulation in Silicon Valley is a microcosm of a global conversation about how to balance innovation with responsibility. As AI continues to advance, finding common ground between these divergent views will be crucial for the sustainable and ethical growth of the technology.
EU AI Act
A crucial technical meeting on the AI Act has unexpectedly unraveled, unveiling a complex web of political intrigue and division.
There is nothing better than some Friday drama to close such a hectic week. A technical meeting on the #AI Act has broken down today, but make no mistake: the issue is deeply political and, if no solution is found soon, the whole law is at risk. A 🧵1/8
— Luca Bertuzzi (@BertuzLuca)
3:20 PM • Nov 10, 2023
OECD's New Definition Set to Shape the EU's AI Act
OECD updates AI definition, influencing EU's AI Act. New criteria focus on machine-based inference and adaptiveness, aligning with global standards.
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has taken a significant step in shaping the future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) regulation by adopting a new definition of AI. This decision, made on November 8, is poised to have a substantial impact on the European Union's forthcoming AI Act, a legislative proposal aimed at regulating AI based on its potential harm.
Originally established to manage the post-World War II Marshall Plan, the OECD has evolved into a key player in international economic collaboration. In 2019, it proposed influential principles for trustworthy AI, including an early AI definition. The recent update to this definition marks a pivotal moment in AI governance, reflecting the latest technological and market developments to enhance clarity, technical accuracy, and future-proofing.
The new definition characterizes AI systems as machine-based systems that infer outputs like predictions, content, recommendations, or decisions from the input they receive. This definition is crucial for the EU's AI Act as it determines the law's scope. The EU aims to align with international standards, including the OECD's definitions, to create a common taxonomy for AI.
One of the notable changes in the updated definition is the removal of the requirement for human-defined objectives. This change acknowledges the evolving nature of AI, where systems can learn new objectives beyond their initial programming. The definition also emphasizes the adaptiveness of AI systems, particularly those based on machine-learning techniques, which can evolve after their design and deployment stages.
FDA
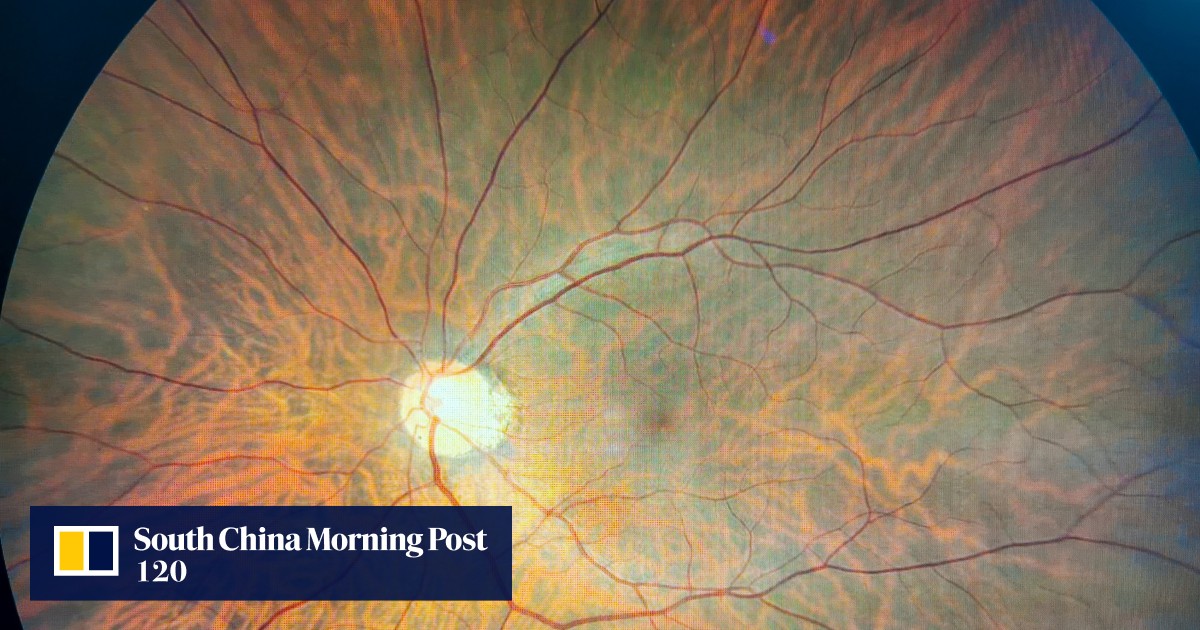
Breakthrough in Cardiovascular Health: FDA Approves Toku’s AI-Powered CLAiR Platform
Toku, Inc., a commercial medical device company specializing in AI and imaging technology, announced a significant milestone with the FDA granting Breakthrough Device designation to its patented CLAiR technology. This platform is poised to become the first in the US market capable of providing affordable, non-invasive, and point-of-care evaluations for cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk using retinal images obtained during routine eye exams.
The CLAiR technology leverages the retina's unique position as a transparent part of the vascular system, allowing easy, non-invasive photography. This AI-powered technology is designed to integrate with existing retinal imaging cameras, providing real-time CVD risk assessments with accuracy comparable to traditional methods. The AI interprets signals from retinal images of blood vessels to identify elevated CVD risk factors such as genetics, hypertension, or high cholesterol.
Healthcare professionals, once the technology is FDA-cleared, will be able to check for elevated cardiovascular risk before the onset of clinical disease. The technology's ability to provide quick and accurate assessments can significantly improve health equity, making quality care and prevention more accessible.
BioXcel Therapeutics' BXCL501 Shows Promise in NIDA-Funded Opioid Withdrawal Trial
Trial for BXCL501, a sublingual formulation of dexmedetomidine aimed at treating opioid use disorder. The trial, coordinated by Columbia University, is a 4-arm study involving 160 patients, with a completion target set for 2024. The urgency of the trial is underscored by the White House's designation of FAAX as an emerging threat. The company is preparing to discuss registrational pathways with the FDA, following promising results where BXCL501 demonstrated tolerability and efficacy in reducing withdrawal symptoms, especially in patients exposed to fentanyl.
The RELEASE trial's topline results were encouraging, showing no severe adverse events and a significant reduction in withdrawal scales at the highest dose. These findings are pivotal as the opioid crisis continues to evolve, with the Biden administration allocating substantial funds to combat the epidemic. BioXcel Therapeutics holds commercialization rights for BXCL501, which is also being explored for other disorders such as PTSD and alcohol use disorder, with funding from government programs.
Partnerships
Terray Therapeutics and NVIDIA: Pioneering AI-Driven Drug Discovery with New Investment and Collaboration
Terray Therapeutics, a biotechnology company specializing in small molecule drug discovery and development, has recently announced a significant equity investment from NVentures, the venture capital arm of NVIDIA. This strategic investment is bolstered by additional financial support from a syndicate of new and existing institutional investors, including notable industry leaders.
The collaboration between Terray and NVIDIA is focused on training foundation models for chemistry, leveraging Terray’s vast experimental data. This initiative is set to enable the use of generative AI in designing optimized small molecule therapeutics, a step forward in the field of drug discovery.
To facilitate this ambitious project, Terray will utilize NVIDIA DGX™ Cloud for developing the world's most comprehensive chemistry foundation models for small molecules. Additionally, some of these models will be accessible on NVIDIA BioNeMo™, a cloud service dedicated to generative AI in drug discovery. This integration with NVIDIA's AI software stack and computing expertise is expected to optimize and scale the development of Terray's foundation models.
Recursion Pharma and Bayer Forge $1.5 Billion Oncology-Focused Alliance, Leveraging AI and Big Data"
Recursion Pharmaceuticals and Bayer have announced a significant shift in their collaboration, now focusing on oncology. This strategic alliance aims to advance up to seven programs, with Recursion potentially receiving up to $1.5 billion based on achieving certain milestones and royalties from net sales. In a parallel development, Recursion has entered a five-year agreement with Tempus, investing $160 million for preferred access to over 20 petabytes of comprehensive oncology data. This data encompasses a wide range of patient-centric information, including DNA, RNA, and health records.
To bolster its drug discovery capabilities, Recursion is significantly upgrading its computational resources. The company is quadrupling the compute capacity of its BioHive-1 supercomputer, integrating over 500 NVIDIA H100 Tensor Core GPUs. This expansion positions BioHive-1 among the world's top 50 supercomputers, marking a substantial leap in Recursion's AI and machine learning capabilities.
NIH Funds Indiana University's AI-Driven Brain Imaging Initiative for Neurological Research
Indiana University has been awarded a $2.3 million grant by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) as part of the BRAIN Initiative 2.0. This significant funding is dedicated to advancing the development of open-source, AI-driven tools for brain imaging research. The primary focus of this initiative is to enhance our understanding of brain networks and their relation to neural computation, using computational tools to analyze diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data.
Central to this project is the DIPY software, an open-source platform for analyzing diffusion MRI data. The NIH grant will be utilized to enhance the tractometry tools in DIPY, enabling comprehensive end-to-end solutions. This will allow neuroscientists to study brain white matter in both healthy individuals and patients with neurological diseases. The project also aims to validate these tools using data from human and non-human primates, ensuring their applicability and accuracy.
Mayo Clinic and IMVARIA Join Forces to Pioneer AI-Driven Biomarker Detection for Lung Cancer
Mayo Clinic, in a groundbreaking collaboration with IMVARIA, is set to develop advanced AI algorithms for detecting software-only biomarkers, initially focusing on lung cancer. This initiative marks a significant leap in cancer diagnosis and treatment, leveraging the power of digital biomarkers to analyze a wide array of medical data, including text, numeric values, and images. The collaboration utilizes Mayo Clinic's vast data sets for algorithm training, combined with IMVARIA's Digital Biomarker Platform. This platform is a game-changer, enabling the development of regulatory-grade digital biomarkers in a fraction of the usual time.
One of the key benefits of this technology is its potential to differentiate early-stage lung cancer or high-risk malignant nodules from benign ones. This differentiation is crucial, as it provides vital prognostic information and assists in making informed treatment decisions. Moreover, the use of digital biomarkers could significantly reduce the need for tissue biopsies, thereby lowering associated risks and costs.
OWKIN and 10x Genomics Join Forces in the MOSAIC Study to Revolutionize Cancer Research with Advanced Spatial Omics
OWKIN, and 10x Genomics, Inc., a pioneer in spatial omics and single-cell technologies, have announced a significant collaboration. This partnership centers around the integration of 10x Genomics' cutting-edge spatial omics and single-cell technologies into the MOSAIC study, a landmark initiative in cancer research.
Launched in June 2023, the MOSAIC project is a $50 million endeavor that aims to revolutionize the understanding of tumor biology. It focuses on mapping tumor structures at an unprecedented single-cell resolution. The project is analyzing an extensive collection of 7,000 tumor samples, which is 100 times larger than any comparable dataset currently available.
Innovation
Owkin's AI Breakthrough in Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis: A Leap Towards Precision Medicine
A recent article in Nature Communications has validated Owkin's innovative AI diagnostic tool, MSIntuit™ CRC, designed for colorectal cancer. This tool marks a significant advancement in the field of oncology, offering a highly sensitive diagnostic approach with a 96% success rate in identifying patients unlikely to respond to checkpoint inhibitor therapy. This development is particularly crucial given the global prevalence of colorectal cancer, which is the third most common cancer worldwide and the second highest cause of cancer mortality.
The study highlights the tool's potential to enhance laboratory efficiency and address the shortage of pathology resources globally. By reducing the testing burden, MSIntuit™ CRC can streamline the diagnostic process, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate therapies faster. This AI-driven tool is a step towards precision medicine, enabling more accurate and efficient diagnosis and treatment of colorectal cancer.
AI's Pivotal Role in Diabetes Management: Transforming Care with Smart Technology
Artificial intelligence is at the forefront of combating insulin resistance, a silent killer that affects nearly half of the adult population globally. Traditional diabetes treatments have fallen short in terms of convenience and efficacy.
AI is changing the game by providing innovative monitoring and groundbreaking treatment options. Effective blood sugar management is crucial, as it can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. New technologies have emerged, allowing patients to monitor their blood glucose levels in a non-intrusive manner. Lifestyle changes, supported by AI-driven apps, have shown to decrease the risk of developing type 2 diabetes substantially.
One such app, 'Nudge,' uses AI to predict imminent blood sugar spikes and suggests personalized activities to mitigate them. This and other commercial solutions like GlucoseZone and mySugr app are part of a growing arsenal against diabetes. Despite the promise, challenges persist, including ensuring data privacy, encouraging technology adoption, and the necessity for accurate data to inform AI recommendations.
A groundbreaking study has introduced an AI model capable of diagnosing type 2 diabetes by analyzing voice recordings. Canadian researchers trained this machine-learning AI to detect 14 distinct vocal differences between individuals with and without diabetes. The AI focused on subtle variations in pitch and intensity, paired with basic health data like age and weight. This innovative approach promises to significantly lower the costs and logistical challenges associated with traditional diabetes diagnosis methods.
The study involved 267 participants from India, comprising both diabetic and nondiabetic individuals. They recorded a specific phrase multiple times over two weeks, resulting in 18,000 recordings. The AI's analysis revealed four key acoustic differences that were particularly effective in diagnosing diabetes, with a higher accuracy rate in women than men.
AI-Powered Breakthrough: Dihydroartemisinin's New Role in Osteoporosis Treatment
Researchers have utilized a deep learning tool to demonstrate the promising potential of Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) in treating osteoporosis, a significant advancement in AI-driven drug discovery. This field has already seen notable successes, such as the repurposing of the arthritis drug baricitinib for COVID-19 treatment and the creation of AI-designed ISM3091 for solid tumor therapy.
The latest development in this arena is the identification of DHA as a potential osteoporosis treatment. By employing a deep-learning-based efficacy prediction system and analyzing bone tissue sequencing, researchers have pinpointed DHA, which could revolutionize osteoporosis treatment. This discovery underscores the growing impact of AI in drug discovery and development, offering new avenues for treating various diseases more efficiently.
AI Retina Scans for Early Alzheimer’s Detection by Hong Kong Scientists
Hong Kong scientists have made a groundbreaking advancement by developing the world's first AI model that can detect Alzheimer's disease through retina scans. This model, created by a team from the Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK) and published in The Lancet Digital Health, showcases an accuracy rate of over 80%. The innovative approach is based on the correlation between Alzheimer’s disease and the retina, although the exact microscopic changes in blood vessels and nerves are yet to be fully understood.
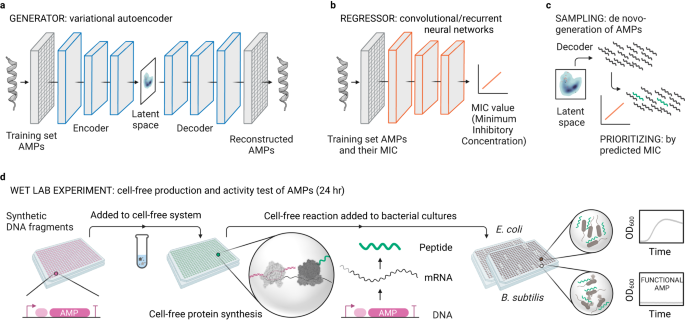
Peptide Production: Deep Learning Meets Rapid Synthesis in Battling Drug-Resistant Pathogens
Bioactive peptide production, particularly antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), are crucial in health and medicine. Leveraging the power of deep learning, researchers have developed a novel cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) pipeline. This method enables the rapid and cost-effective production of AMPs directly from DNA templates, a breakthrough in peptide synthesis.
The research team utilized deep learning algorithms to design thousands of AMPs de novo. From these, 500 candidates were selected through computational methods for further production and screening using the CFPS pipeline. This high-throughput approach led to the identification of 30 functional AMPs. These peptides were then subjected to extensive characterization, including molecular dynamics simulations, antimicrobial activity assessments, and toxicity evaluations.
Remarkably, six of these newly developed AMPs demonstrated broad-spectrum activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens. More importantly, these peptides did not lead to the development of bacterial resistance, addressing a significant challenge in current antimicrobial treatments.
The study's findings underscore the potential of combining computational design with rapid synthesis techniques. The CFPS pipeline, in particular, stands out for its ability to produce and test bioactive peptides within less than 24 hours, a feat that could revolutionize the field. This approach not only accelerates the discovery and development of new AMPs but also offers a cost-effective solution to the growing issue of drug-resistant pathogens.
Trends
Generative AI's Influence on Digital Health Investment: Insights from GSR Ventures Survey
87% of digital health investors say generative AI sways their strategies, per GSR Ventures.
A recent online survey conducted by GSR Ventures, a digital health investment firm, has revealed a significant impact of generative AI on investment strategies within the digital health sector. The survey, which included over 40 participants from leading investment firms, highlighted several key trends and expectations for the remainder of 2023. Notably, a majority of investors anticipate maintaining or increasing their technology investments compared to 2022, despite expecting lower valuations for early-stage companies.
The oncology specialty emerged as the most promising area for startups, with cardiovascular care also receiving considerable interest. Conversely, ophthalmology was identified as offering the least opportunity. The survey pinpointed the healthcare provider shortage and burnout crisis, along with changing reimbursement models, as the most pressing challenges that startups could address.
Report underscored the influence of generative AI, noting that it is 'significantly' shaping investment strategies.
Google's Strategic Leap into Healthcare: AI Innovations and Cloud Computing Transformations
Google, recognizing the potential in healthcare, has embarked on a comprehensive strategy to integrate its technological prowess into this sector. With a staggering 70,000 health-related searches per minute, Google's move towards healthcare seems a natural progression. The acquisition of Fitbit for $2.1 billion and the development of the Med-PaLM AI model underscore its serious commitment.
The company's AI initiatives, such as C2D2 for colonoscopy improvements and a mammography AI system, demonstrate its capability to enhance medical diagnostics. Particularly noteworthy is Med-PaLM, a healthcare-specific AI model, which has shown remarkable accuracy and is now accessible to a wider range of healthcare professionals.
Google's cloud computing ventures are equally significant, offering smaller healthcare practices access to advanced AI without the need for expensive hardware. This approach democratizes high-level medical technology, making it more accessible and efficient.
However, Google's journey hasn't been without challenges. The FDA's rejection of Verily’s wearable for Parkinson’s monitoring highlights the regulatory hurdles the company faces. Moreover, Google Health's pivot from consumer tech to focusing on AI, remote monitoring, and cloud computing indicates a strategic refocusing in response to the evolving market and regulatory landscape.
Optimizing Hospital Efficiency: UCHealth's AI-Driven Transformation in Patient Flow Management
The concept of operational digital transformation :
Where healthcare organizations, like UCHealth, are leveraging the vast amount of data from electronic medical records (EMR) and other IT systems. By applying complex mathematical algorithms to this data, hospitals can gain timely and actionable insights that enhance the quality, effectiveness, and efficiency of care.
UCHealth's implementation of AI and workflow automation tools, specifically iQueue for Inpatient Flow, is a prime example. This technology enables the prediction of discharges and admissions on an hourly basis, ensuring optimal bed allocation and uncovering bottlenecks in admission and discharge processes.
The results have been significant, with a reduction in the average length of stay by 0.4 days, equivalent to adding 35 inpatient beds, and enabling 1,380 more patient admissions, a 6.8% increase, without the need for additional physical beds or staff.
ImmunoInformatics has issued a call for papers for a special issue titled "Spatial immunology and immuno-oncology: computational methods and applications." This initiative seeks to explore the intricate spatial architecture within tissue microenvironments, which holds critical biomedical significance.
The journal invites literature reviews and research articles that provide insights into the spatial organization of immune cells and their interactions within these environments, utilizing high-throughput molecular profiling and multiplexed imaging technologies.
Authors are encouraged to submit their manuscripts by December 15, 2023, with the editorial acceptance deadline set for March 1, 2024.